close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 47 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2022-07-26 Origin: Site






Ginsenoside is the active ingredient in ginseng and is also a steroidal compound that is mainly found in ginseng medicinal herbs. Ginsenoside Rg1, is the root of the plant Ginseng of the Family Pentagram, which has suggested that it has the effect of promoting hippocampal neurogenesis, improving neuroplasticity, enhancing learning memory, anti-inflammatory, auxiliary anti-tumor, etc., and has broad application prospects in high-end health care, auxiliary anti-tumor, prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease and so on.

Ginsenoside is the active ingredient in ginseng and is also a steroidal compound that is mainly found in ginseng medicinal herbs. Ginsenoside Rg1, is the root of the plant Ginseng of the Family Pentagram, which has suggested that it has the effect of promoting hippocampal neurogenesis, improving neuroplasticity, enhancing learning memory, anti-inflammatory, auxiliary anti-tumor, etc., and has broad application prospects in high-end health care, auxiliary anti-tumor, prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease and so on.
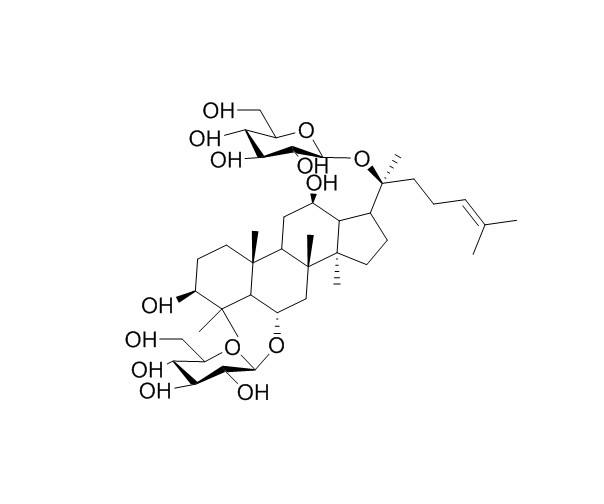
The researchers investigated the role of Rg1 on rat adjuvant arthritis (AIA, whose pathological manifestations are similar to those of human rheumatoid arthritis and are commonly used to study human rheumatoid arthritis) and the mechanisms within it to explore the effect of Rg1 on rheumatoid arthritis. The results showed that Rg1 had a therapeutic effect on AIA rats, and its mechanism may be related to the anti-inflammatory effect of upregulating PPAR-γ and subsequent inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
The researchers observed AIA rats after a dose of 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection for 14 days. The results showed that Rg1 significantly reduced joint swelling and injury. In addition, Rg1 can also significantly reduce TNF-α levels and IL-6 levels in RAW264.7 cells stimulated by inflammatory joints and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in AIA rats, increase PPAR-γ protein expression, inhibit IκBα phosphorylation and NF-κB nucleus shift.